Black Box Testing
Black Box Testing
- Black-box testing also called behavioral testing,
- It focuses on the functional requirements of the software.
- Functional testing of a component of a system
- Examine behavior through inputs & the corresponding outputs.
- Input is properly accepted, output is correctly produced.
- Black-box testing attempts to find errors in the following categories:
- (1) Incorrect or missing functions
- (2) Interface errors
- (3) Errors in data structures or external database access
- (4) Behavior or performance errors
- (5) initialization and termination errors
- Black box testing is used during the later stages of testing after
white box testing has been performed.
- Different Black box testing techniques
- (1) Graph Based Testing Methods
- (2) Equivalence Partitioning
- (3) Boundary Value Analysis
- (4) Orthogonal Array Testing
Black box testing techniques - (1) Graph-Based Testing Methods
- The first step in black-box testing is to understand the objects that are
modeled in software and the relationships that connect these objects.
- Once this has been accomplished, the next step is to define a series of
tests that verify “all objects have the expected relationship to one
another”.
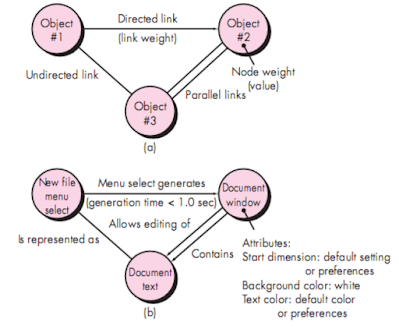
- Graph Representation
- A collection of nodes that represent objects,
- Links that represent the relationships between objects,
- Node weights that describe the properties of a node (e.g., a
specific data value or state behavior),
- Link weights that describe some characteristic of a link.
- The symbolic representation of a graph is shown in Figure.
- Nodes are represented as circles connected by links that take a
number of different forms.
- A directed link (represented by an arrow) indicates that a
relationship moves in only one direction.
- A bidirectional link, also called a symmetric link, implies that the
relationship applies in both directions.
- Parallel links are used when a number of different relationships are
established between graph nodes.
Black box testing techniques - (2) Equivalence Partitioning Method
- Equivalence partitioning is a black-box testing method that
divides the input domain of a program into classes of data from
which test cases can be derived.
- An equivalence class represents a set of valid or invalid states for
input conditions.
- Equivalence classes guidelines
- If an input condition specifies a range,
- one valid and two invalid equivalence classes are defined
- Input range: 1 – 10 Eq classes: {1..10}, {x < 1}, {x > 10}
- If an input condition requires a specific value,
- one valid and two invalid equivalence classes are defined
- Input value: 250 Eq classes: {250}, {x < 250}, {x > 250}
- If an input condition specifies a member of a set,
- one valid and one invalid equivalence class are defined
- Input set: {-2.5, 7.3, 8.4} Eq classes: {-2.5, 7.3, 8.4}, {any other
x}
- If an input condition is a Boolean value,
- one valid and one invalid class are define
- Input: {true condition} Eq classes: {true condition}, {false
condition}
Black box testing techniques - (3) Boundary Value Analysis Technique
- A greater number of errors occurs at the boundaries of the input domain.
- It is for this reason that boundary value analysis (BVA) has been developed as a
testing technique
- Test both sides of each boundary
- Look at output boundaries for test cases
- Test min, min-1, max, max+1, typical values
- Example : 1 <= x <=100
- Valid : 1, 2, 99, 100
- Invalid : 0 and 101
- Guidelines for BVA
- If an input condition specifies a range bounded by values a and b, test cases
should be designed with values a and b and just above and just below a and
b.
- If an input condition specifies a number of values, test cases should be
developed that exercise the minimum and maximum numbers. Values just
above and below minimum and maximum are also tested.
Black box testing techniques - (4) Orthogonal Array Testing
- Orthogonal array testing can be applied to problems in which the
input domain is relatively small but too large to accommodate
complete testing.
- The orthogonal array testing method is particularly useful in
finding region faults — an error category associated with faulty
logic within a software component.
- Consider a system that has three input items, X, Y, and Z. Each of
these input items has three discrete values associated with it.
There are 3^3 = 27 possible test cases.
- Phadke suggests a geometric view of the possible test
cases associated with X, Y, and Z illustrated in Figure…
- Used when the number of input parameters is
small and the values that each of the
parameters may take are clearly

- To illustrate the use of the L9 orthogonal array, consider the send
function for a fax application.
- Four parameters, P1, P2, P3, and P4, are passed to the send function.
For example : Function (p1,p2,p3,p4)
- Each takes on three discrete values P1 takes on values:
- P1 = 1, send it now
- P1 := 2, send it one hour later
- P1 = 3, send it after midnight
- P2, P3, and P4 would also take on values of 1, 2, and 3, signifying
other send functions.
- If a “one input item at a time” testing strategy were chosen, the
following sequence of tests (P1, P2, P3, P4) would be specified: (1, 1,
1, 1), (2, 1, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1, 1), (1, 2, 1, 1), (1, 3, 1, 1), (1, 1, 2, 1), (1, 1, 3,
1), (1, 1, 1, 2), and (1, 1, 1, 3).
The L9orthogonal array testing approach enables you to
provide good test coverage with far fewer test cases than the
exhaustive strategy
Black Box Testing - Advantage & Disadvantages
- Advantage
- Find missing functionality
- Independent from code size and functionality.
- Disadvantages
- No systematic search for low level errors.
- Specification errors not found.




With that being said, I am very excited to meet the head of banks, Fintech and crypto investors who dream of disrupting the Fintech arena.
ReplyDeleteIf you are one of those individuals, let’s explore ideas together.
Ankit Jain - Join me on my journey to disrupt the Fintech field and create a frictionless banking experience for upcoming generations.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete